Reviewing Pull Requests
This guide assumes you already have your own clone of the repository based on your own fork (or the main project).
If you are someone in charge of reviewing pull requests for an open source repository on GitHub (like a tech lead), you'll need to know how to review pull requests. This guide will help you understand the process of reviewing pull requests and how to provide feedback to contributors.
Viewing Pull Requests
To view pull requests, navigate to the repository on GitHub and click on the "Pull Requests" tab. This will show you a list of all open pull requests for the repository. Click on a pull request to view the details.
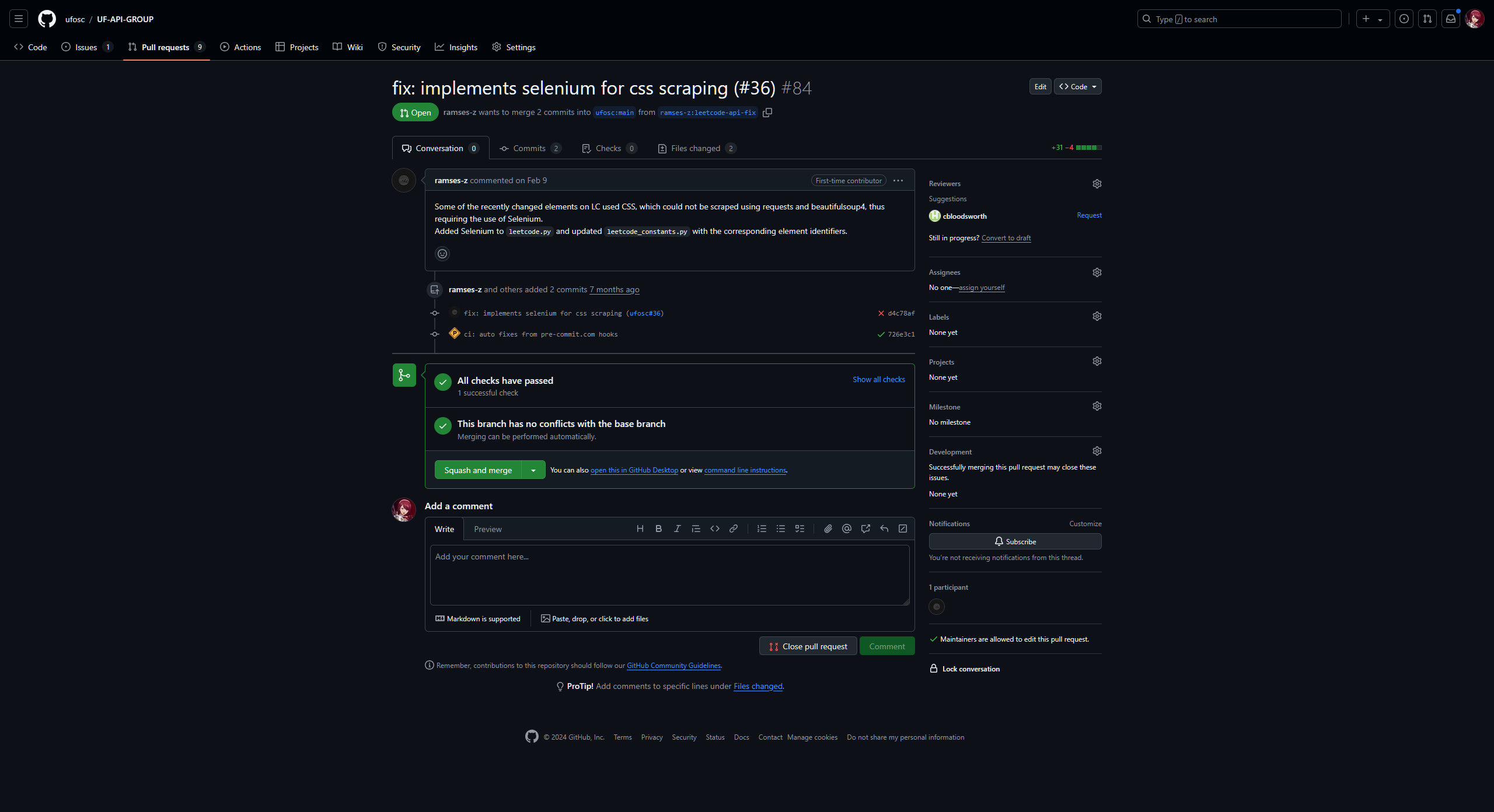
There are a number of elements to look at here:
- The main page of the pull request, which shows the title, description, and any comments.
- The commits section, which shows the commits that are part of the pull request.
- The checks section, which shows the status of any automated checks (e.g., CI/CD pipelines).
- And finally, the files changed section, which shows the changes made in the pull request.
The last section is the most important, as it shows the actual changes that the contributor has made.
Files Changed Section
On the file changed section, you can review these changes by clicking on individual files and viewing the diff (the changes made to the file).
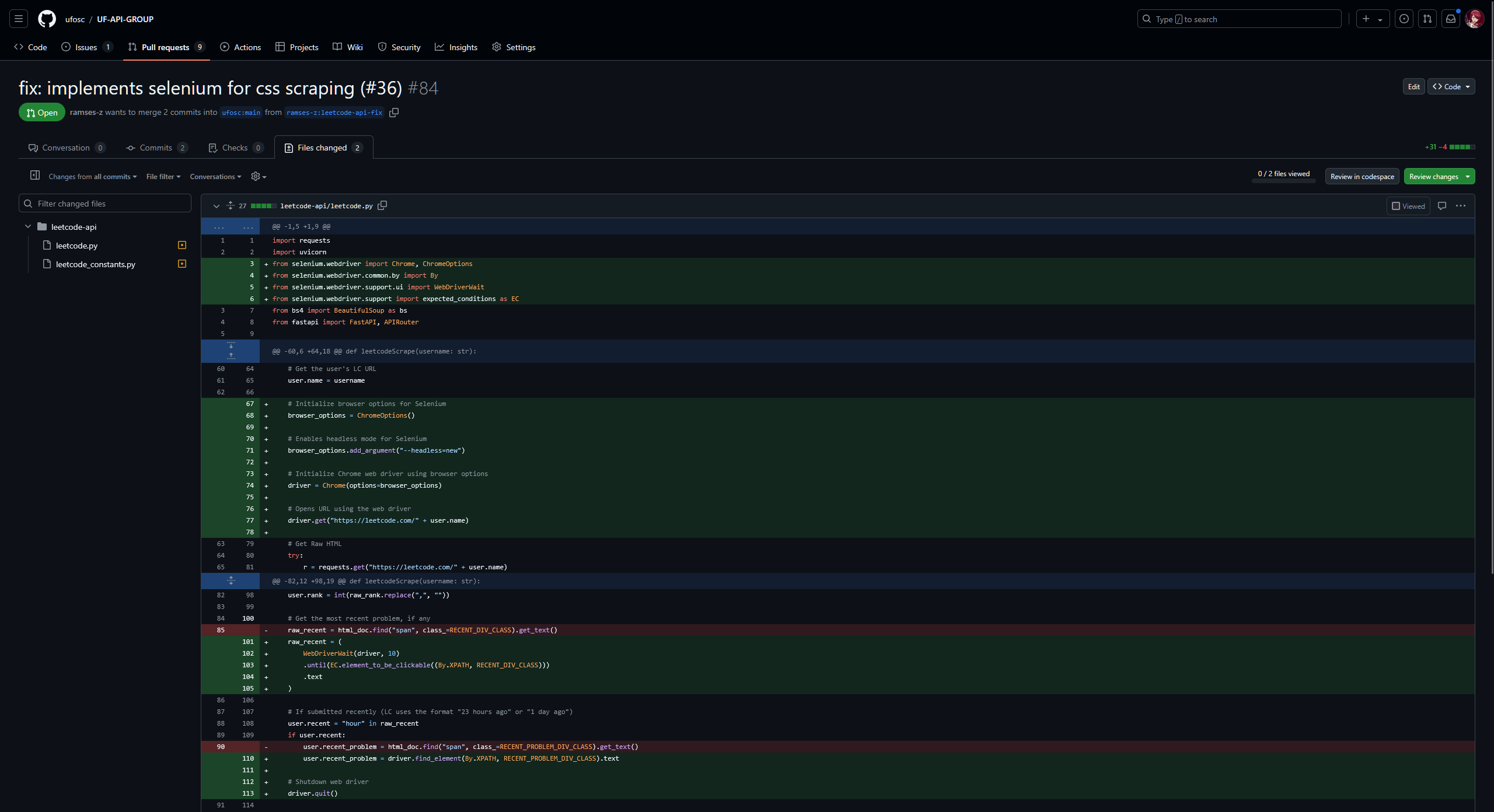
A very core feature about GitHub is that you can comment on individual lines of code. This is very useful for providing feedback to contributors. If you hover over a line of code, you'll see a blue "+" button that allows you to add a comment.
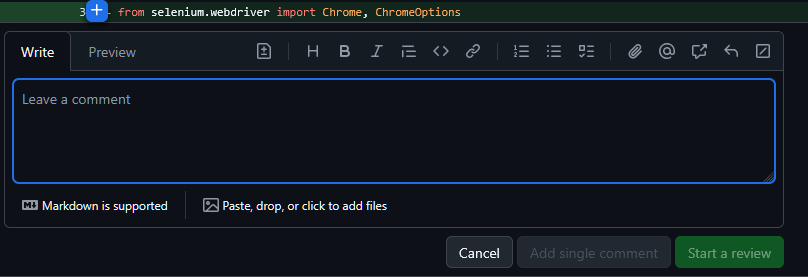
To select multiple lines, click and drag to highlight the lines you want to comment on.
When you do this, you'll notice a comment box appear. You can type your feedback here and submit it. Note that there are two options for submitting:
- Add single comment: This will allow you to submit a comment without starting a review.
- Start a review: This will allow you to submit a review with your comments.
Pretty frequently, you'll want to start a review, as this will allow you to submit multiple comments at once and do some special behavior.
Reviewing Pull Requests
To start a PR review, simply make a comment on the PR and press the "Start a review" button. This will allow you to submit a review with your comments.
Make as many comments as you need to provide feedback to the contributor. Be sure to be clear and concise in your feedback, and provide suggestions for improvement where necessary.
Finally, once you are finished (or if you have no comments you wish to add to any particular line of code), you can go to the "Finish your review" (or "Review changes") button at the top right of the page.
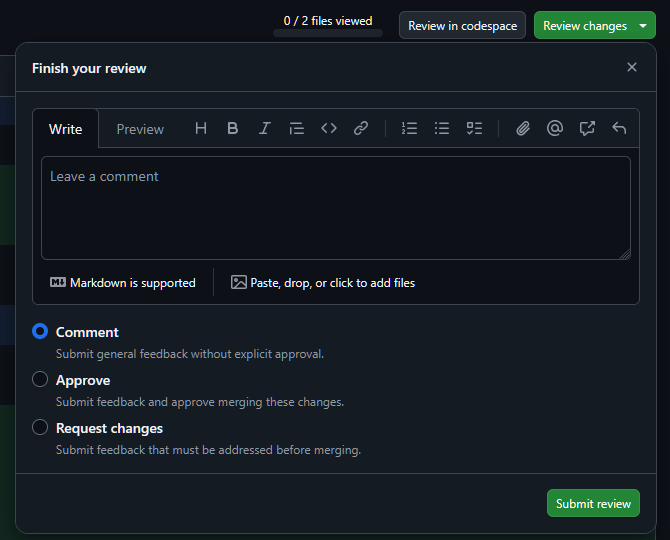
Here, you can submit a final review with an overall comment and approve or request changes to the pull request. The review will then appear on the pull request page for the contributor to see.
Testing Pull Requests
While the above steps are important, it's also important to test the changes made in the pull request. This usually involves running the code locally and checking that it works as expected.
To do that, head to their fork of the repository and get its URL:
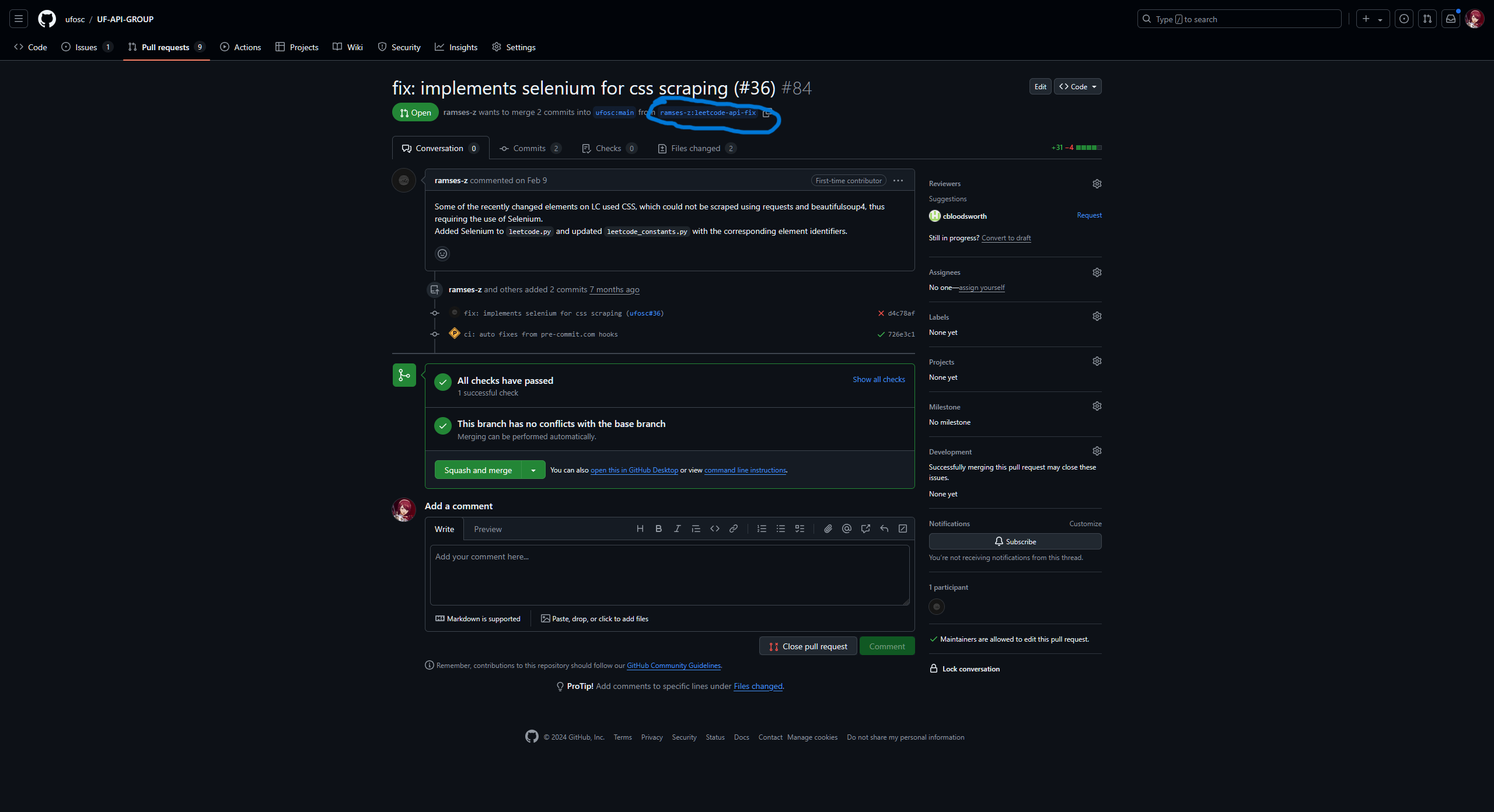
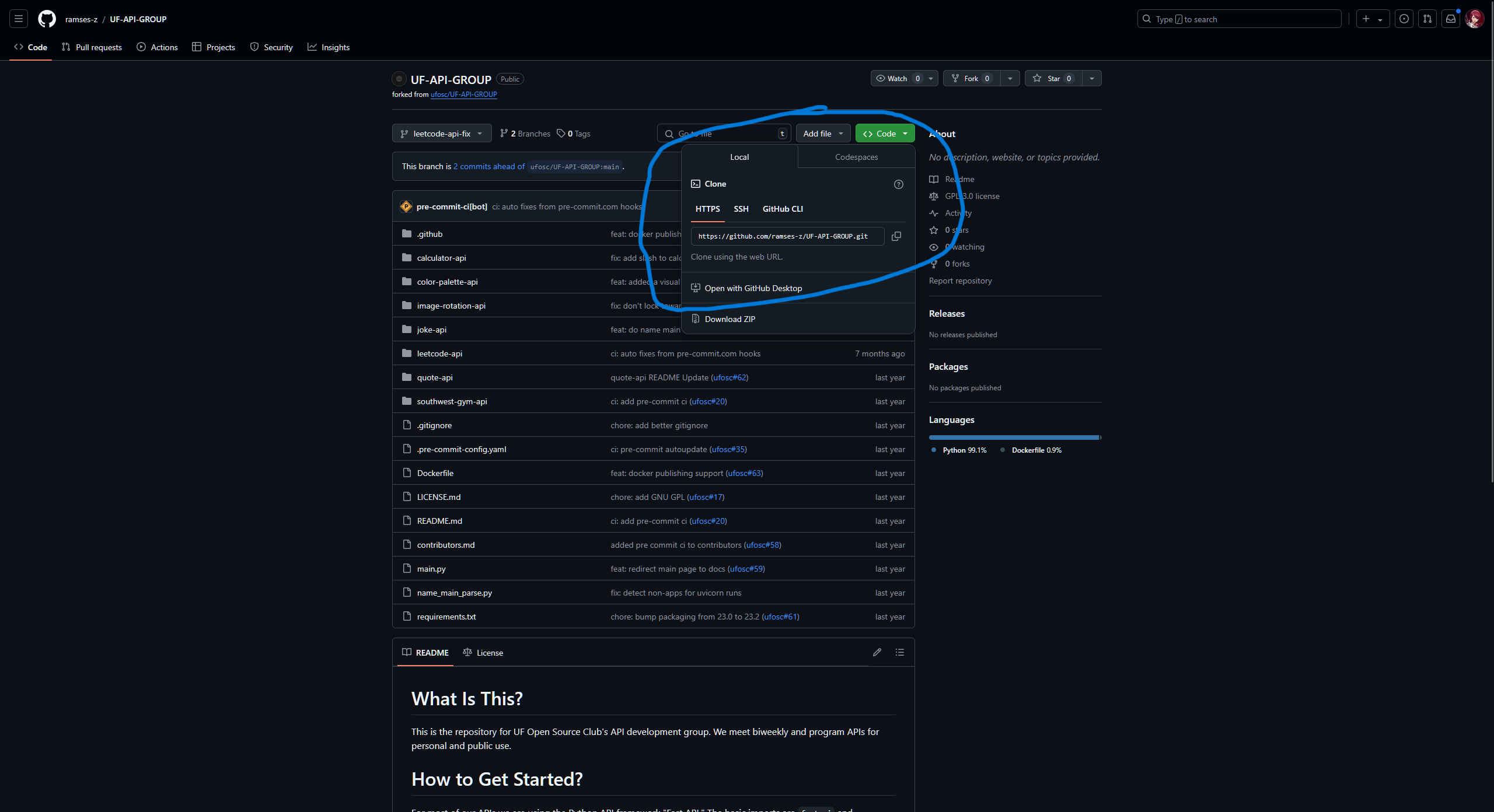
Then, go to where your clone of the repository is and add a new remote:
git remote add <any name that isn't "origin"> <URL of contributor's fork>
For example, I did git remote add ramses-z https://github.com/ramses-z/UF-API-GROUP.git.
After that, you can pull the changes from the contributor's fork:
git pull <name of the remote>
For example, I did git pull ramses-z.
Finally, you can make a new local branch that tracks the contributor's branch:
git switch -c <whatever branch name you want> <name of the remote>/<branch name>
For example, I did git switch -c ramses-z/leetcode-api-fix ramses-z/leetcode-api-fix.

You now are working directly with their code, and can test it out locally. If you find any issues, you can go back to the PR and request changes.
Finally, if everything is good, you can switch back to your main branch and delete the branch you made:
git switch main # or whatever your main branch is
git branch -d <branch name>
Merging Pull Requests
Once you have reviewed and tested the pull request, you can merge it into the main branch. To do this, you can go back to the pull request page and click the "Merge pull request" button.
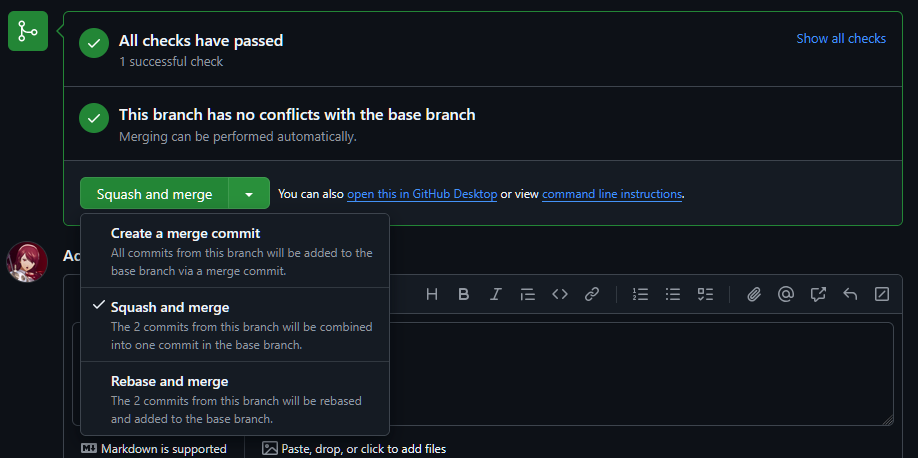
In the above image, the dropdown button next to the main button has been clicked to demonstrate some options. These include:
- "Create a merge commit": This will create a new commit that merges the changes from the pull request into the main branch. All of the previous commits from the pull request will be preserved.
- "Squash and merge": This will squash all the commits from the pull request into a single commit and merge it into the main branch. This is useful if the pull request has multiple commits that you want to combine into a single commit.
- "Rebase and merge": This will rebase the changes from the pull request onto the main branch and merge them. This only works if there's no conflicts. However, this means that there is no merge commit, which can make the history cleaner.
Choose the appropriate option and click the "Confirm merge" button to merge the pull request.